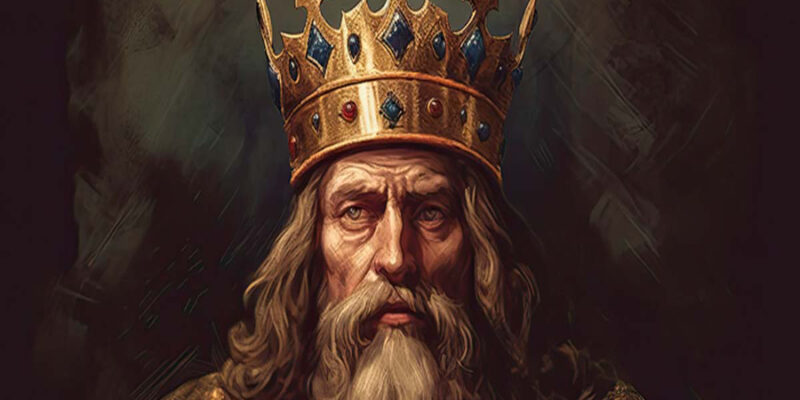
Charlemagne, also known as Charles the Great, stands out as a transformative figure whose actions reshaped the course of Western and Central Europe following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire.
Conquest and Unification
Born into a lineage known for its military prowess, Charlemagne’s conquests spanned vast territories, encompassing regions such as France, northern Italy, Germany, Austria, Spain, the Netherlands, Poland, and more. His efforts to unify Western Europe earned him the title “Father of Europe” and are celebrated as a monumental achievement in history.
Linguistic Influence
Charlemagne’s influence extended beyond military conquests, leaving a lasting mark on linguistic development in Western Europe. Many languages in the region adopted words for “king” derived from his name, reflecting his significant impact on the cultural and linguistic landscape of the continent.
Imperial Coronation and Cultural Revival
In a historic moment, Charlemagne was crowned Emperor of Rome by Pope Leo III, symbolizing his ambition to establish a unified empire. His reign also witnessed a cultural renaissance known as the Carolingian Renaissance, characterized by educational reforms, the establishment of libraries, and the preservation of classical texts. Charlemagne’s commitment to literacy ensured the transmission of knowledge and culture to future generations.
Enduring Legacy
Charlemagne’s legacy persists in various aspects of modern Europe, serving as a foundational figure in the continent’s history. From the depiction of the King of Hearts in playing cards to the foundational principles of European identity, his influence remains pervasive. Despite his death at the age of 71, Charlemagne’s imprint on European history endures, solidifying his status as a key architect of the European narrative.









Comments